Specialized Salivary Care
Specialized Salivary Care
Find comfort with our minimally invasive techniques
UTHealth Houston Salivary Stone Program
A UTHealth Houston Salivary Stone Program specialist diagnoses and treats salivary gland problems related to salivary stones, duct stenosis, as well as inflammation and tumors to provide you everyday relief. Our board-certified physician has the tools and expertise to try and improve or eliminate symptoms with minimally invasive techniques, prevent unnecessary gland restrictions, minimize nerve damage, and improve your quality of life.
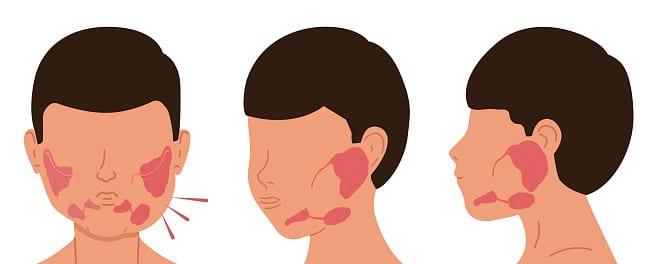
What are salivary duct stones?
Salivary duct stones (sialolithiasis) are hardened mineral deposits that form in the salivary glands and are the most common cause of salivary gland swelling. Salivary duct stones can also cause stenosis (narrowing or obstruction). Stenosis could be also caused by some inflammatory conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome.
Symptoms
Salivary duct stones and stenosis usually affect the major salivary glands.
- Gland swelling
- Pain or discomfort while eating
- Obstruction of saliva production and flow
Salivary obstruction may cause a bacterial infection due to growth, inflammation, and abscess formation that causes severe pain and swelling.
How we diagnose
Our physician will conduct a physical examination of the salivary glands and ducts, and discuss any history of intermittent gland swelling and pain while eating. Approximately 80 percent of cases are usually visible as calcified deposits or dilation of the duct before the obstruction.
Common disorders
- Intermittent swelling of parotid and submandibular glands
- Stones of parotid and submandibular glands
- Narrowing of the ducts of parotid and submandibular glands
- Recurrent swelling of salivary gland due to Sjögren’s syndrome and other inflammatory disorders
- Obstruction of the salivary ducts due to radioactive iodine treatment
- Small tumors originating from the salivary ducts
How we treat
Sialendoscopy
Sialendoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical technique, provides a more accurate diagnosis and treatment of the condition. In this procedure, a very small endoscope is introduced into the salivary duct to visualize the stones and stenosis. Salivary stones could be removed under visualization by using small baskets going through the endoscope. Larger stones may be broken endoscopically with the help of very small wire drills or lasers. In more rare and complex situations, a hybrid procedure could be done with the combination of sialendoscopy and open surgery.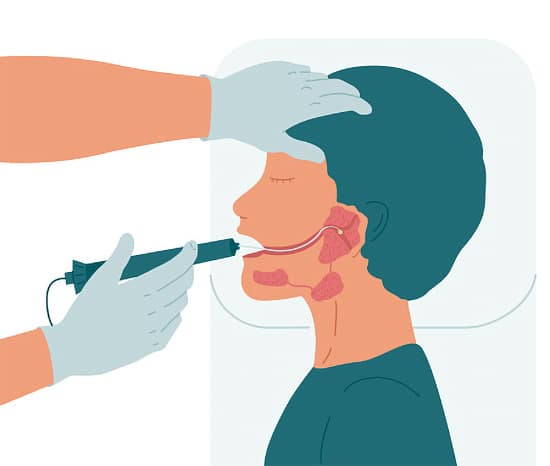
Benefits
- Accurate diagnosis of salivary duct disorders like stones and stenosis
- Very high success rate in treatment of salivary stones, obstruction, or other inflammatory diseases
- Preservation of the salivary gland, preventing unnecessary removal
- Minimizing the risks of complications due to open gland surgeries, like facial nerve paralysis, lip droop, tongue paralysis, or decreased sensation at the floor of the mouth
Minimally Invasive Techniques
- Diagnostic sialendoscopy
- Sialendoscopic removal of salivary stones with baskets or other instruments
- Sialendoscopic dilation of the salivary duct obstructions
- Balloon dilation of the narrow ducts
- Sialendoscopic salivary stone breaking
- Transoral stone removal
- Plastic repair of salivary ducts, stenting or reorientation
- Transfacial removal of parotid duct stones
Patient Success Stories
Jim Connors Benefits from Minimally Invasive Sialendoscopy
Jim Connors, 62, had problems off and on for nearly a decade and took antibiotics or sucked on lemon drops to dilate the parotid duct and relieve the obstruction. Beginning in March 2020, his cheek remained swollen. An ultrasound ordered by his primary care physician appeared normal, as did a subsequent CT scan. In 2020, Sancak Yuksel, MD, a board-certified otorhinolaryngologist at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, was able to remove the salivary duct stones and dilate the salivary gland using the minimally invasive basket technique.
-Aster Kebreab
Meet our physician

Sancak Yuksel, MD
Sancak Yuksel, MD, is an Associate Professor in the Department of Otorhinolaryngology. He obtained his medical degree at the Hacettepe University School of Medicine in Ankara, Turkey, and completed his Otorhinolaryngology residency at the Istanbul University Cerrahpasa School of Medicine in Istanbul, Turkey. After residency, he also received advanced training in Head-Neck and Skull Base Surgery as a fellow in the same department. Dr. Yuksel served as a research fellow in the Basic Science Laboratory of the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, and worked in numerous NIH-funded projects focused on the middle ear and the eustachian tube pathophysiology. He completed a two-year clinical fellowship in the Department of Pediatric Otolaryngology at Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. He also served as an instructor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. Dr. Yuksel is a member of American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. His clinical interests include adult and pediatric ear diseases, adult and pediatric cochlear implantation, sialendoscopy and salivary gland disorders, newborn and pediatric swallowing and airway problems, and congenital head and neck lesions.
UT Physicians Otorhinolaryngology - Texas Medical Center
Houston, TX, 77030-1539




